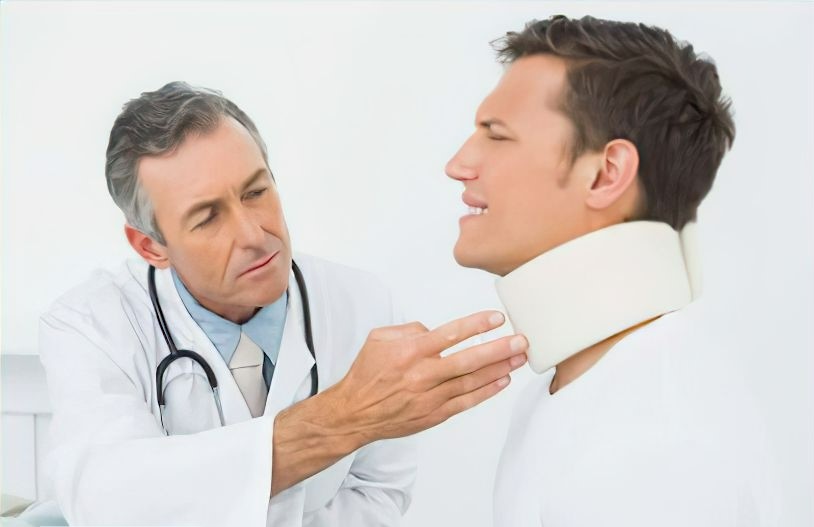
Can Whiplash Cause Brain Injury
Many car accident victims are relieved to discover that they have not sustained any broken bones upon leaving the emergency room. After enduring months or even years of soft tissue injuries, these victims would willingly trade their whiplash injury for a broken bone. With over thirty years of experience in personal injury law, I can confidently say that a soft tissue injury is often more severe than a simple fracture. The term ‘soft’ in ‘soft tissue’ refers to the nature of the tissue itself, not the injury. For instance, the brain is composed of soft tissue, and can whiplash cause brain injury far from insignificant or ‘soft.
Casting can facilitate the healing of a wrist fracture in approximately four weeks, while an ankle fracture typically takes eight weeks to heal. Conversely, soft tissue injuries such as ligament, muscle, or tendon ruptures or tears may require months to heal. These injuries can result in chronic pain or a permanently restricted range of motion. During the healing process, scar tissue forms to repair the soft tissues. However, this scar tissue is less flexible than our muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Additionally, a muscle, tendon, or ligament injury can disrupt the nerves in and around the soft tissues, leading to pain, numbness, and tingling. In some cases, permanent disability may ensue.
The term “whiplash” is sometimes associated with ambulance-chasing lawyers who hastily treat their new clients. However, whiplash is not a one-time injury and can evolve into a chronic condition that causes persistent headaches and discomfort.
Statistics reveal that more than 3,000,000 Americans suffer from whiplash injuries each year, with approximately half of them experiencing chronic pain and around 10% becoming permanently disabled.
Since the 1950s, the medical community has conducted over 80 studies to determine the likelihood of whiplash victims developing serious complications. Between 45% and 83% of individuals develop chronic pain, with neck pain and headaches being the typical symptoms.
Several risk factors contribute to a poor prognosis, including prior neck injury, prior headaches, prior neck pain, inadequate headrest, poor seating position in the car, arthritis, degenerative disc disease, advanced age, rear impact, female gender, and lack of awareness of an impending crash.
Consequently, around 3,000,000 whiplash victims endure chronic pain annually, and 10% of those injured experience permanent disability.
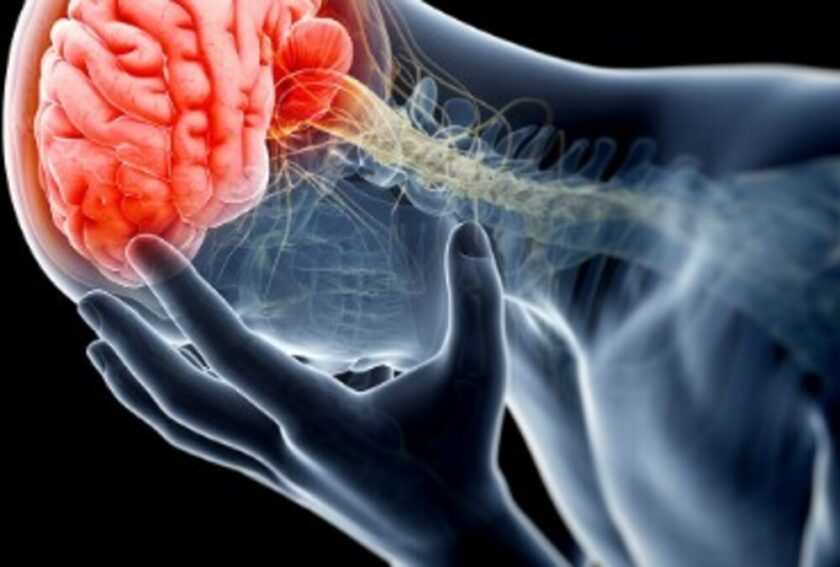
Previously, the medical community downplayed the severity and long-term effects of whiplash injuries, including headaches and cognitive issues. However, they now acknowledge that a typical whiplash injury, resulting from rapid acceleration followed by braking (typically in a rear-end collision), is one of the leading causes of mild traumatic brain injuries or concussions. The interior of the skull contains bony ridges, while the brain resembles Jello in a bowl. During sudden acceleration or deceleration, the brain forcefully moves back and forth against the rigid, bony contours of the skull, leading to stretching and shearing of brain tissue. This process causes microscopic damage that may or may not fully recover. Diffuse axonal injury, a hallmark of mild traumatic brain injuries can result in cognitive deficits, memory problems, and even personality changes. Unfortunately, diffuse axonal damage cannot be detected through standard MRI or CT scans. Therefore, the absence of visible damage on these scans does not rule out the possibility of a serious injury.
Medical literature suggests that even brief alterations in consciousness, such as appearing dazed, startled, or confused, can indicate widespread neuronal dysfunction. Mild brain injuries can lead to structural neuronal damage, as evidenced by findings in patients who appeared to have minor or trivial brain injuries. These findings include destruction of myelin around axons, axonal retraction bulbs (ruptured axon ends), and small reactive glial cell aggregates indicating recent injury in various brain regions (Jonathan M. Silver M.D. et al., Neuropsychiatry of traumatic brain injury, American Psychiatric Press Inc.).
A concussion, a mild traumatic brain injury, can occur without losing consciousness. In fact, the modern definition of concussion encompasses any change in the mental state resulting from a blow to the head or an acceleration/deceleration injury (such as whiplash). In the past, professional football players were removed from matches only when they lost consciousness. However, medical professionals now consider a person to have suffered a concussion if they appear dazed, confused, or startled. It is now widely recognized that multiple concussions can cause serious brain injuries, even in the absence of unconsciousness.
SCHEDULE A CONSULTATION
Experience a pain-free life! Call us at (727) 268-0172
When involved in an auto accident, it is crucial to seek treatment for any physical injuries sustained, such as whiplash, through physical therapy, chiropractic treatments, and/or anti-inflammatory medications. Additionally, it is important to pay attention to any cognitive impairments experienced by yourself or your loved ones following the crash. Watch out for headaches, fatigue, light sensitivity, changes in personality, and mood swings, as these are classic symptoms of concussions and post-concussion syndrome. Failure to address these symptoms promptly can lead to more severe consequences.
Aside from the well-known phenomena of diffuse axonal injuries, which cause structural damage to brain tissue, neurons, and blood vessels, it has been established that a blow to the head or the rapid acceleration/deceleration associated with whiplash injuries triggers a complex molecular cascade that results in secondary damage to the brain. One of these chemical reactions is oxidative stress, wherein the body produces excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) following trauma. Excess ROS is also found in Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s. This chemical cascade and the subsequent release of certain brain chemicals can lead to emotional, cognitive, and memory issues in whiplash victims. Unfortunately, these chemical reactions and diffuse axonal damage are not visible on standard imaging scans. These injuries are real, and patients with concussions often experience depression due to chronic headaches, fatigue, memory problems, cognitive difficulties, emotional distress, and other post-concussion symptoms. Insurance companies may wrongfully attribute these symptoms to depression, labeling the accident victim as a malingerer rather than recognizing the true cause of their condition.
Whiplash and mild traumatic brain injuries are not insignificant, soft, or mild injuries. Relying solely on a primary care physician for treatment may prolong the recovery process. Such injuries often require the expertise of a neurologist or physiatrist with specialized training and experience in handling such cases. It is essential to seek appropriate referrals for you and your family.
Book a Consultation
If you or a loved one is seeking alternative treatment options for brain injury after car accident Florida Medical Pain Management offers Ketamine infusion therapy as a potential solution. Ketamine infusion has shown promising results in helping individuals with TBI manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Discover the potential of Ketamine infusion therapy for TBI and embark on a path toward healing and recovery. Contact us today!
Our Treatment Services
Florida Medical Pain Management’s top priority is to serve our patient’s needs and create long-lasting relationships with them. Our treatments include:
- Treatment for Neuropathy
- Arthritis Management
- Back Pain Medication
- Chronic Pain Treatments
- PRP Injections
- Epidural Injection
- Regenerative Medicine
- Hip Pain Medication
- Ketamine Infusion Therapy
We want to help patients live more fulfilling and productive lives by effectively managing their pain. Florida Medical Pain Management also provides home therapy and many more. Click here to see our other services.